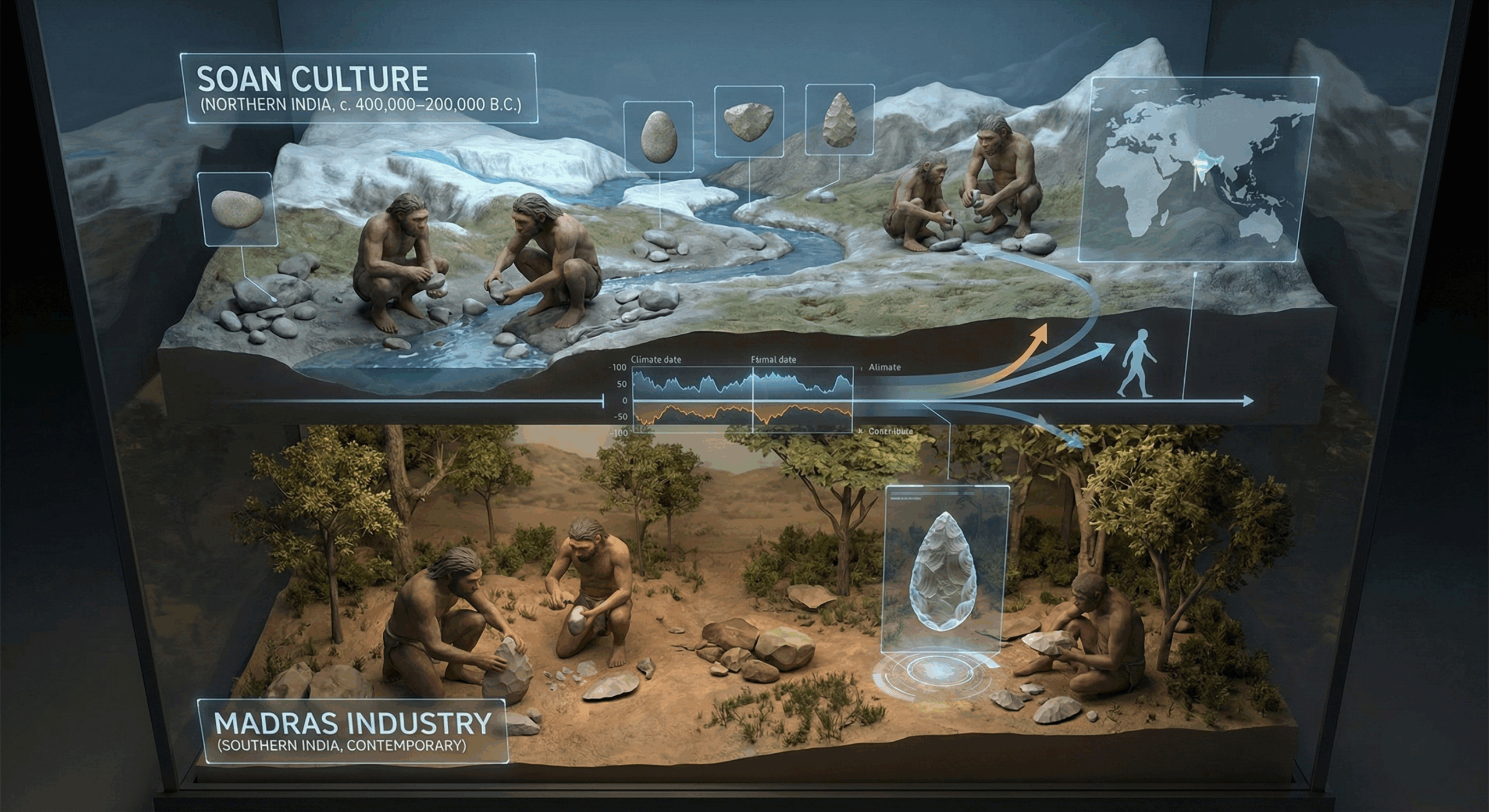
The Soan and Madras industry related to stone age times in Indian sub-continent.
The Logic of Time: Clock as an Essential Reasoning Topic
INTRODUCTION
Time is one of the most important dimensions of human life. From waking up in the morning to going to sleep at night, every activity revolves around time. To measure, understand, and manage time, humans invented clocks. Over centuries, clocks have evolved from simple sundials to highly precise atomic clocks.
In logical reasoning, especially in competitive examinations, the topic of Clock plays a crucial role. Questions based on clocks test a candidate’s understanding of angles, relative motion, speed, logical thinking, mathematical reasoning, and visualization skills.
Clock problems may look simple at first glance, but they often involve tricky concepts such as:
- Relative speed of hands
- Angle between hands
- Coinciding, overlapping, and opposite positions
- Gain or loss of time
- Mirror image of clocks
Because of this, clock questions are considered high-scoring but concept-sensitive. With proper understanding and practice, a student can solve these questions quickly and accurately.
DEFINITION
A clock is a device used to measure, keep, and indicate time, usually in hours, minutes, and seconds.
In reasoning and aptitude, clock problems deal with:
- The movement of the hour hand, minute hand, and sometimes second hand.
- The angle formed between these hands at a given time.
- The relative position of the hands at specific intervals.
- Time calculation when clocks gain or lose time.
- Mirror and water image interpretation of clock time.
Key Components of an Analog Clock:
- Dial: Circular face divided into 12 equal parts.
- Hour Hand: Short hand, completes one round in 12 hours.
- Minute Hand: Long hand, completes one round in 60 minutes.
- Second Hand: Thin hand, completes one round in 60 seconds.
Types of Clock Problems with Examples and Solutions
Clock problems can be broadly classified into the following types:
Type 1: Angle Between Hour Hand and Minute Hand,
Full circle = 360°
Clock has 12 divisions
Each division = 30°
Movement Speeds
Hour hand = 0.5° per minute
Minute hand = 6° per minute
Basic Concept
Formula
Angle = (30H – 11/2M)
Where, H = hour(from 1 to 12), M = minutes(from 0 to 59
Example: Find the angle between the hour and minute hands at 3:20.
Solution:
30(H) – 11/2 (M)
30(3)-11/2(20)
90-110
Answer: 20°
Type 2: When Hands Coincide (Overlap)
Hands coincide 11 times in 12 hours
Time gap between coincidences: (65/11) minutes.
Example: How many times do the hands of a clock coincide in 24 hours?
Solution:
In 12 hours → 11 times
In 24 hours → 22 times
Answer: 22 times
Type 3: When Hands are Opposite (180° Apart)
Hands are opposite 11 times in 12 hours
Example: How many times are the hands opposite in a day?
Solution:
In 24 hours → 22 times
Type 4: When Hands are at Right Angle (90°)
Occurs 22 times in 12 hours
Example: How many times do the hands form a right angle in 24 hours?
Solution:
In 12 hours → 22 times
In 24 hours → 44 times
Type 5: Gaining or Losing Time
Some clocks run fast or slow.
Formula
(Correct time) ={ (Shown time) 60 } / { 60 (+or-) (gain or loss) }
Example: A clock gains 5 minutes every hour. What will it show after 6 hours if it was set correctly?
Solution:
Gain in 6 hours = 30 minutes
Answer: 6.30
Type 6: Mirror Image of Clock
Formula
{Mirror time} = 11:60 – (Actual time)
Example: What is the mirror image of 4:35?
Solution:
11:60 − 4:35
Answer: 7:25
Some Other Example
Question: At what time between 5 and 6 o’clock will the hands of a clock be together?
Solution:
Let the time be 5 : x minutes
Position of hour hand:
(5 *30) + (0.5x) = 150 + 0.5x
Position of minute hand: 6x
For coincidence:
150 + 0.5x = 6x
150 = 5.5x
x = {150/5.5}
x= {300/11}
Answer: 5:(300/11)
Question: How many degrees does the minute hand gain over the hour hand in 1 minute?
Solution:
Minute hand speed = 6° per minute
Hour hand speed = 0.5° per minute
6−0.5=5.5°
Answer: 5.5° per minute
Question: What is the mirror image of 3:40?
Solution:
Mirror time formula: 11:60−given time
11:60−3:40
= 8:20
Answer: 8:20
Question: At what time between 7 and 8 o’clock are the hands opposite?
Solution:
Formula: {(h×60)+30}/11
={ (7×60)+30}/11
= 450/11
Answer: 7:40 10/11
Question: A clock gains 5 minutes per hour. How much will it gain in 24 hours?
Soluiton:
5×24=120 minutes
120 minutes = 2 hours
Answer: 2 hours
IMPORTANT TRICKS
1. Angle per minute
Minute hand → 6°
Hour hand → 0.5°
2. Coincidence interval
(65/11) minutes
3. Opposite interval
(65/11) minutes
4. Right angle interval
(6/22) minutes
5. Mirror Image Shortcut
11:60 – {Given time}
Use Of Clock In Real Life
1. Time Management- Planning daily activities
2. Transportation- Trains, flights, buses
3. Education- Exam duration, schedules
4. Medical Field- Monitoring treatment intervals
5. Sports- Timing races and matches
6. Technology- Computer processors, satellites
7. Navigation- GPS and astronomy
Understanding clock logic helps in punctuality, discipline, and productivity.
why clock is important in reasoning
1. Tests analytical ability
2. Improves calculation speed
3. Enhances visual imagination
4. Frequently asked in exams
5. Easy scoring topic with practice
6. Builds foundation for time & work and speed-distance-time
CLOSING STATEMENT
Clock problems may appear challenging initially, but once the basic concepts, formulas, and tricks are mastered, they become one of the easiest and fastest topics to solve in reasoning. Consistent practice transforms complexity into clarity.
CONCLUSION
The topic of Clock in reasoning is a perfect blend of mathematics and logic. It strengthens conceptual thinking and sharpens mental calculation skills. From basic angle problems to advanced time-loss calculations, clock reasoning develops precision and confidence.
For competitive exams, mastering this topic can significantly boost overall scores. With the right approach, formulas, and practice, clock questions can be solved accurately within seconds.