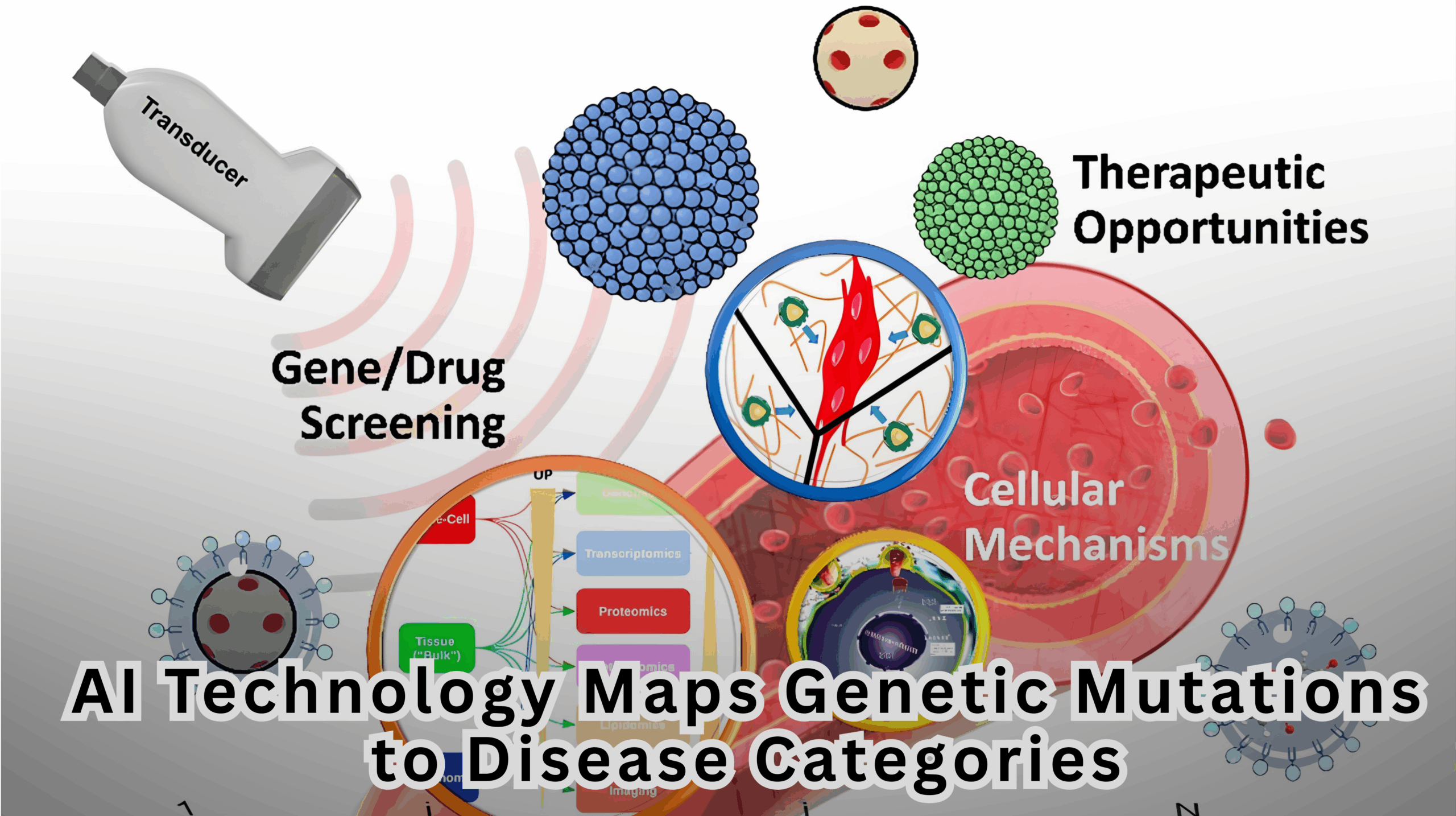
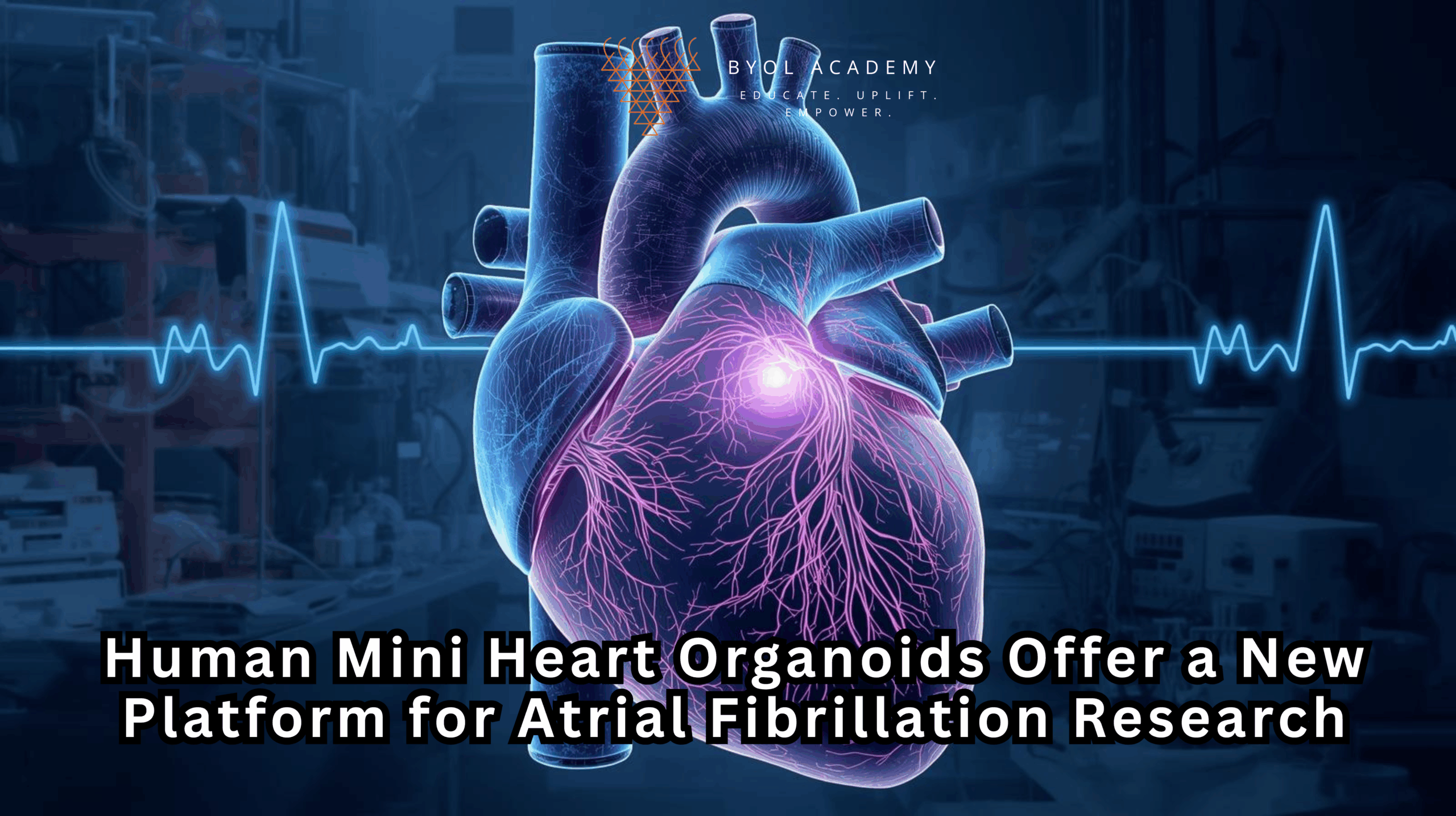
Cancer continues to impose a substantial clinical and societal burden, ranking among the leading causes of death worldwide and in […]
Ranking in Reasoning: Concepts, Methods and Solved Examples

INTRODUCTION
Reasoning is one of the most essential abilities required for cracking competitive examinations, solving real life problems, and making logical decisions. Among the various branches of reasoning such as verbal reasoning, non verbal reasoning, analytical reasoning, and logical reasoning the concept of Ranking holds a very important position. Ranking based questions test an individual’s ability to analyze positions, compare information, establish relationships among objects or people, and deduce correct results based on given conditions.
Ranking questions are widely used in exams like SSC, Banking, Railway, Police, Defence, and many state level competitive exams. This is because ranking helps evaluators judge how well a candidate can interpret ordinal positions, reason backward or forward, and understand relational placement. If approached correctly, ranking is one of the easiest and most scoring topics in the reasoning section.
This article explains ranking in detail its definition, types, examples, applications in real life, importance, and more. It will guide students or learners to understand ranking from basic to advanced level.
DEFINITION
Ranking in reasoning refers to determining the position or order of persons, objects, numbers, or events based on certain conditions. These conditions may be related to:
- Height
- Weight
- Marks
- Age
- Performance
- Sequence
- Left–right or top–bottom placement
Ranking establishes the ordinal position of items in a group. Unlike quantitative values, ranking deals with relative positions. It helps us answer questions such as:
- Who is first?
- Who is last?
- What is the position of A from the left?
- How many people are between B and C?
- If ranks change after rearrangement, what is the new position?
In simple words, ranking is the process of arranging items in a structured order and identifying their correct positions.
Types Of Ranking
Ranking questions come in several varieties. Understanding each type makes the topic easier.
(A) Simple Ranking (Single Direction)
This involves ranking either from the left, right, top, or bottom. You are directly given the position of a person or object.
Example : Rohan is 7th from the left in a row of 20 students.
Question: In a class, Ritu is 9th from the left end. If there are 30 students in the row, what is her position from the right end?
Solution: Position from right = Total students – Position from left + 1
= 30 – 9 + 1
= 22
Answer: Ritu is 22nd from the right.
(B) Dual or Two Directional Ranking
Here, you are given both left and right (or top and bottom) positions, and you may need to find the total number of persons.
Example: A is 5th from the left and 7th from the right.
Question: A student is 8th from the left and 7th from the right. Find the total number of students.
Solution: Total = Left position + Right position – 1
= 8 + 7 – 1
= 14
Answer: There are 14 students.
(C) Ranking with Middle/Between Positions
These questions involve finding how many people are between two persons.
Question: Arjun is 10th from the left. Manoj is 18th from the left. How many students are between them?
Solution: Between them = 18 − 10 − 1 = 7
Answer: 7 students are between Arjun and Manoj.
Example 4: Person Between Left and Right End
Question: A girl is 6th from the left and 15th from the right in a row. How many students are there in total, and how many are between her and the ends?
Solution: Total = 6 + 15 − 1
= 20
Students to the left end before her = 6 − 1 = 5
Students to the right end after her = 15 − 1 = 14
Answer: Total students = 20
Between her and ends: 5 on left, 14 on right.
(D) Position Interchange or Swapping Ranking
In these questions, two persons interchange their positions, and you must find their new ranks.
Question: In a row of 25 boys, Ravi is 6th from the left, and Mohan is 10th from the right. If they interchange their positions, what will be Ravi’s new position?
Solution: First, find Mohan’s original left position:
Left position = Total − Right position + 1
= 25 − 10 + 1
= 16
When they swap: Ravi goes to Mohan’s position → Ravi’s new rank = 16th from left
Answer: Ravi’s new position is 16th from the left.
(E) Comparison Based Ranking
These questions give comparative information like: A is taller than B, B is taller than C, etc.
You determine the final order.
Question : In a class, A is taller than B but shorter than C. D is the shortest. Arrange.
Answer : C > A > B > D
(F) Puzzle-Based Ranking
These are more complex and may include ranking as a part of seating arrangement or puzzle problems.
(G) Age/Height/Marks Ranking
Used to compare quantities who is the youngest, tallest, or scored highest.
Example : Ranking by Height
Question: Amit is taller than Rohan but shorter than Suresh. Rohan is taller than Punit. Who is the shortest?
Solution: Arrange them in order:
Suresh > Amit > Rohan > Punit
Answer: Punit is the shortest.
Example : Ranking in Exams (Marks)
Question: In a class of 50 students, Neha scored the highest marks. Riya scored more than Tanvi but less than Neha. Tanvi scored more than Meera. Who is second in the class?
Solution: Order: Neha > Riya > Tanvi > Meera
Answer: Riya is second.
(H) Circular/Vertical Ranking
Ranking in a circular arrangement or in top–bottom vertical lists.
Tips, Tricks & Shortcuts (With Examples & Solutions)
Ranking problems become very easy when you know short formulas, common patterns, and logical shortcuts. Below are the most useful ones.
TRICK 1: Total = Left Rank + Right Rank – 1
This is the MOST IMPORTANT formula in ranking.
Formula: {Total Persons= (Left position of Person + Right Position of Person) – 1}
Example 1: A boy is 7th from the left and 10th from the right. How many boys are there?
Solution: Total = 7 + 10 − 1 = 16
Answer: 16 boys
TRICK 2: Finding Position From Opposite Side
If you know the position from left, you can find from right using:
{Right Position = (Total) – (Left Position) + 1}
Example 2: In a line of 30 students, Priya is 8th from the left. What is her position from the right?
Solution: Right = 30 − 8 + 1 = 23
Answer: 23rd from right
TRICK 3: Number of People Between Two Persons
If both ranks are from the SAME side: { Between = (First Person – Second Person) – 1 }
Example 3: A is 12th from the left, B is 19th from the left. How many people are between them?
Solution: Between = 19 − 12 − 1 = 6
Answer: 6 people
TRICK 4: If Ranks are from Opposite Sides
Use total: { Between = (Total) – (Rank1 from Left) – (Rank2 from Right) }
Example 4: In a row of 40 students:, A is 10th from left, B is 12th from right. How many students between A and B?
Solution: Between = 40 − 10 − 12 = 18
Answer: 18 students
TRICK 5: When Two People Swap Positions
Use opposite-side formula.
Example 5: In a row of 20: Ravi = 5th from left, Mohan = 6th from right. Find Ravi’s new position if they interchange.
Step 1- Convert Mohan’s rank to left side:
{ From left = (Total) – (From right) + 1}
Left = 20 − 6 + 1 = 15
Step 2 – Ravi moves to Mohan’s previous position:
Ravi’s new rank = 15th from left
TRICK 6: Finding Position from Middle
Middle = (Total + 1) ÷ 2
Example 6: In a row of 21 boys, what is the middle position?
Solution: Middle = (21 + 1) ÷ 2 = 11
Answer: 11th is middle
TRICK 7: Ranking by Comparison (Height/Age/Marks)
Use table format quickly:
Example 7: A > B, C > A, D < B
Find tallest.
Solution:
C > A > B > D
C is the tallest
TRICK 8: When Total Is Not Given
Use the same formula backward: { Total = Left + Right – 1}
Example 8: A is 9th from left and 15th from right. What is total?
Solution:
9 + 15 – 1 = 23
Total = 23
TRICK 9: If Positions Change After Addition or Removal
Use difference method: { New Rank = (Old Rank) + (People Added Before) }
Example 9: A is 7th in a class. If 3 new students join before him, what is his new rank?
Solution: New rank = 7 + 3 = 10
Answer: 10th
TRICK 10: Shortcut for Between When Last Ranks Are Given
If ranks are from opposite sides and total not given:
Case Formula: { Total = Left + Right + Between }
Example 10: A is 5th from left, B is 4th from right between 10 Find total.
Solution: Total = 5 + 4 + 10 = 19
Answer: 19
EXTRA TRICKS (High-Scoring in Exams)
TRICK 11: Faster Arrangement Mental Model
Always draw a short line and mark ranks as dots. Helps avoid confusion.
TRICK 12: Always Convert Opposite Rank to Same Side
Opposite → convert → solve.
TRICK 13: If Two are on Extreme Ends
Check if ends change after swapping or adding.
TRICK 14: Always Check if Positions Overlap
If L + R – 1 > total → question is incorrect.
TRICK 15: For complicated comparison questions
Arranging vertically is easier:
Example: Rank (1st), Rank (2nd), Rank (3rd)
5. Use of Ranking in Real Life
- Ranking is not limited to competitive exams; it plays a major role in everyday life.
(a) Education
- Students are ranked by marks in class.
- Entrance exams use rank lists for admissions.
(b) SportsPlayers are ranked based on performance.
In tournaments, teams are ranked by points.
(c) Job Recruitment
- Candidates are ranked by scores in exams or interviews.
(d) Military and Government
- Officers follow hierarchical ranks.
(e) Health and Fitness
- Doctors rank symptoms to diagnose seriousness.
- Fitness trainers rank exercises by difficulty.
(f) Business and Corporate Sector
- Employees are ranked based on performance.
- Products are ranked based on sales, ratings, and reviews.
(g) Daily Decision-Making
- Choosing the best mobile phone by comparing features.
- Ranking grocery items based on price and quality.
- Prioritizing tasks in daily life.
- Ranking helps us evaluate options and make logical choices.
6. Why It’s Important
Ranking is important for several reasons:
(a) Enhances Logical Thinking: It trains the brain to organize information and find patterns.
(b) Develops Comparative Skills: Ranking questions help compare multiple items simultaneously.
(c) Improves Decision Making: Understanding ranking helps in choosing the best option from available alternatives.
(d) Essential for Competitive Exams: Since ranking is a scoring topic, mastering it improves overall performance.(e) Builds Analytical Ability: It strengthens the ability to analyze relative positions and deduce conclusions.
(f) Useful in Planning and Prioritizing: Ranking helps people plan their work according to importance and urgency.
(g) Strengthens Problem-Solving Skills: It increases efficiency in solving real life and academic problems. In short, ranking is essential for exams, jobs, real life situations, and personal development.
7. Closing Statement
Ranking is one of those reasoning topics that may look simple at first glance but is deeply connected to analytical thinking and real-world decision-making. Whether you are a student preparing for exams or a professional solving problems at work, ranking concepts guide your reasoning process. Mastering ranking strengthens your cognitive skills and dramatically improves problem-solving efficiency.
8. Conclusion
Ranking plays a crucial role not only in reasoning examinations but also in various walks of life. It develops clarity of thought, improves logical judgment, and enhances decision-making capabilities. From classrooms to corporate boardrooms, from sports fields to government offices ranking is used everywhere. Therefore, understanding how ranking works, its different types, and how to solve ranking-based problems is important for overall intellectual growth.
If practiced properly, ranking becomes one of the most rewarding and scoring topics in competitive exams. The steps, examples, and explanations covered in this article provide a detailed guide to understanding ranking thoroughly.